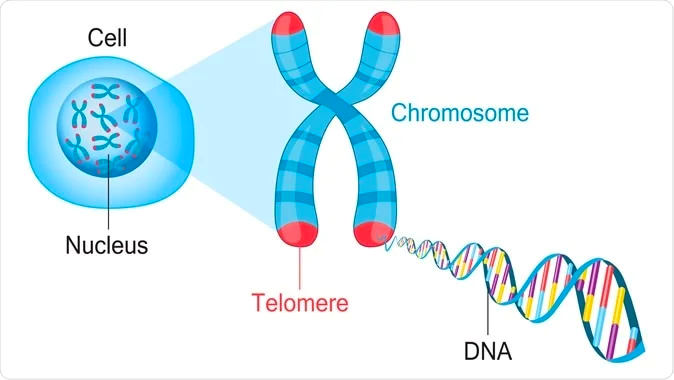
Telomere Attrition
Telomere attrition is a hallmark of aging that refers to the shortening of telomeres, which are the protective caps on the ends of chromosomes. Telomeres play a critical role in maintaining the stability of the genome and protecting DNA from damage. With each cell division, telomeres become shorter, eventually leading to cellular senescence or cell death.
Telomere attrition is important because it is thought to contribute to the aging process and the development of age-related diseases. As telomeres become shorter, cells become more vulnerable to DNA damage, which can lead to cellular dysfunction and contribute to the development of diseases such as cancer. In addition, shortened telomeres have been linked to a range of age-related diseases, including cardiovascular disease, dementia, and diabetes.
The role of telomere attrition in aging is complex and not fully understood. However, it is thought that telomere shortening contributes to the decline in physiological function that characterizes aging. This may be due to the loss of key cellular processes, such as stem cell function and immune system function, that are necessary for maintaining tissue homeostasis
There are several strategies that have been proposed to address telomere attrition and promote healthy aging. One approach is to enhance telomerase activity, which is the enzyme responsible for maintaining telomere length. This has been shown to slow down telomere shortening and promote cellular longevity in some studies. Another potential strategy is to reduce exposure to factors that contribute to telomere shortening, such as oxidative stress and inflammation.
In addition, lifestyle factors have been shown to play a role in telomere length maintenance. For example, regular exercise has been associated with longer telomere length, while smoking and poor diet have been associated with shorter telomeres. Therefore, adopting healthy lifestyle habits may also help to promote healthy aging and protect against telomere attrition.
Telomere attrition is one of the 12 hallmarks of aging that can contribute to cellular dysfunction and the development of age-related diseases. While the mechanisms underlying telomere attrition and its role in aging are complex and not fully understood, strategies to address telomere attrition, such as enhancing telomerase activity and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, show promise as potential interventions for promoting healthy aging.