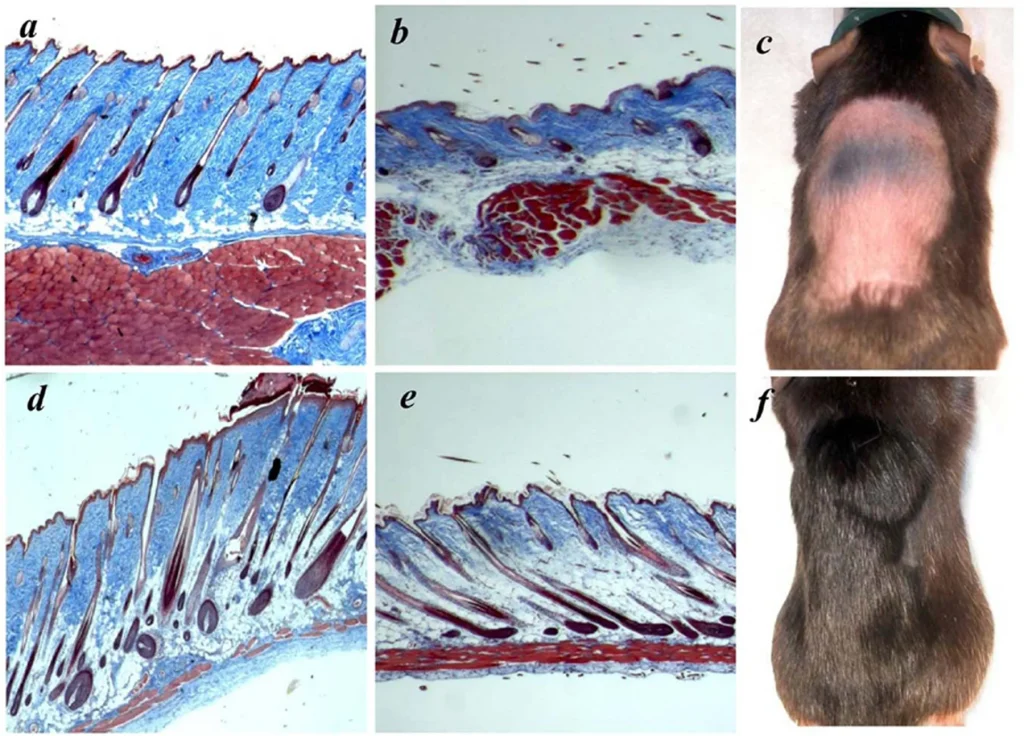
Multi-Organ Membrane Repair and Dopamine Balancing.
“Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 antagonizes the incidence of a series of gastrointestinal lesions, it has a positive impact on the healing processes of various wounds, a proven angiogenic effect, protective effect on endothelium and it modulates synthesis of NO.” (1)”Apart from the effects on various gastrointestinal lesions, the potentially beneficial effect on pancreas, liver injuries, endothelium and heart damage, i.e. dysrhythmias following reoxygenation, and blood pressure, along with effect on experimental acute/chronic inflammation, wound and fracture (pseudoarthrosis) healing are described. It appears that these beneficial effects all together provide a particular network reflecting activity of a special peptidergic defence system.” (4)”In support of this concept, it appears that there are interactions of this pentadecapeptide with many important systems (namely, dopamine-, NO-, prostaglandin-, somatosensory neurone-systems), that could provide a basis for the observed protective effects. Moreover, since disturbance of these systems’ functions (i.e. dopamine-, NO-, somatosensory neuronal-system) which manifest either over-activity or as inhibition, may contribute to the multiple lesions in different organs. The reported evidence that this pentadecapeptide is able to counteract both their over-action, and their inhibition, may suggest this pentadecapeptide as a new, but most probably essential physiological defence system and that should be further investigated.” (4)