Sermorelin vs Ipamorelin and Tesamorelin
Sermorelin, Ipamorelin, and Tesamorelin are all peptides that stimulate the release of growth hormone (GH) in the body, but they have some differences in terms of their mechanisms of action and thus the overall effects that they cause. Sermorelin is a synthetic peptide that works by stimulating the secretion of growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) from the hypothalamus. GHRH, in turn, triggers the release of growth hormone from the pituitary gland. Sermorelin is well known for extending growth hormone peaks and increasing growth hormone trough levels. It generally does not increase GH peaks, meaning it does not cause supraphysiologic levels of GH.Ipamorelin is a synthetic peptide that specifically targets the ghrelin/growth hormone secretagogue receptor. It stimulates the release of growth hormone directly from the pituitary gland. It is known for causing very large spikes in GH levels, well above normal physiologic peaks. It is a short-lived peptide, however, and so the GH spikes are short-lived as well.Tesamorelin is a synthetic peptide that is similar in structure to human growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH). It stimulates the release of growth hormone from the pituitary gland. Tesamorelin is used clinically for reducing adiposity (fat tissue) and is more similar to Sermorelin than it is to Ipamorelin. Like Sermorelin, it extends the length of time that GH peaks last, but does not generally cause supraphysiologic GH levels.Sermorelin and Tesamorelin are the most similar, but it would be mistake to conflate the properties of these two peptides. Despite the fact that both are GHRH analogues and thus stimulate the release of GH from the anterior pituitary, there are profound differences in overall outcomes produced by these peptides. Whereas Tesamorelin tends to produce weight loss via targeting of fat mass, Sermorelin tends to favor muscle building and balanced fat burning resulting in body composition change, but not necessarily a huge change in weight.These differences are just one example of how peptides from the same class can differ from one another based on simple structural changes made to their amino acid sequences. Researchers have, for years now, been investigating how these subtle changes influence target effects, half-life, off-target effects, bioavailability and other features of these peptides. Now, with enough different growth hormone regulators on the market, research is starting to shift to investigate how combinations of these peptides stack up to one another. Here is a look at how Sermorelin on its own might compare to a combination of Ipamorelin and Tesamorelin.
Sermorelin vs Ipamorelin and Tesamorelin | Growth Hormone Profiles
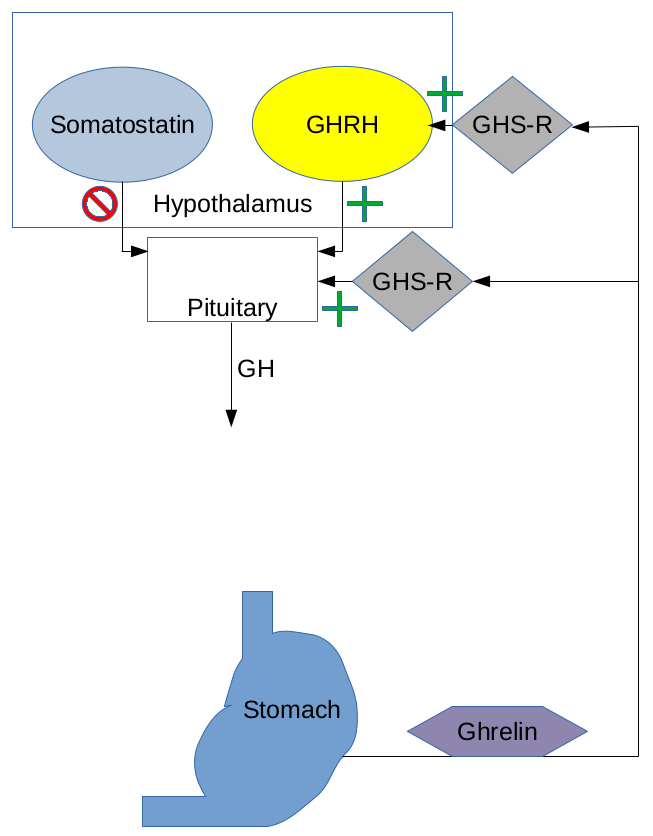
The primary action of all of these peptides is to influence levels of circulating growth hormone. Tesamorelin and Sermorelin do this by acting on the GHRH receptor while Ipamorelin influences GH levels by acting on the ghrelin or growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHS-R). The receptors that these peptides target in addition to how they bind to their specific receptors determines their impact on growth hormone levels.
Sermorelin is very similar in structure to GHRH and thus is similar in function as well. Research shows that Sermorelin can lead to an increase in GH with peak levels occurring about 30 minutes to a few hours after administration. On average, studies have reported GH increases in the range of 2 to 10 times the baseline GH levels following Sermorelin administration, with once-daily administration resulting in increases that are on the lower end of that spectrum. One of the benefits of using Sermorelin is that it promotes a natural, pulsatile release of GH. The body’s natural GH secretion occurs in a pulsatile fashion, with several peaks and troughs throughout the day. Sermorelin therapy aims to replicate this pattern, which is essential for the body’s overall growth and maintenance. Maintenance of pulsatile GH release is one of the primary keys to avoiding off-target effects.
Ipamorelin is a ghrelin mimetic and as such binds to the GHS-R. In clinical and research studies, Ipamorelin has been shown to increase GH levels, but the magnitude of the increase can vary. Typically, after the administration of Ipamorelin, there is a rapid spike in GH levels, and this peak can reach levels several times higher than baseline. Of the three peptides here, Ipamorelin is the most likely to cause massive, but short-lived increases in GH levels. This, of course, makes Ipamorelin useful when targeted GH peaks need to be timed with something like exercise, food intake, or sleep.
The increase in GH levels after Ipamorelin administration tends to be dose-dependent, meaning that higher doses are generally associated with a more significant GH response. The frequency and timing of Ipamorelin administration can also influence GH release. As a short-acting peptide, Ipamorelin can be dosed more frequently than Sermorelin to achieve net increases in GH levels. This is made possible not just by Ipamorelin’s short half-life, but by its near total lack of off-target effects. Ipamorelin is widely regarded in research circles as the most specific of the growth hormone secretagogues and as having the fewest off-target effects.
Tesamorelin is a GHRH analogue. Studies of Tesamorelin have shown that it can lead to an increase in growth hormone levels and this increase is generally within a physiologically normal range. The specific increase in GH levels can depend on factors such as the individual’s baseline GH levels, the dosage of Tesamorelin administered, and the duration of treatment. Like Sermorelin, Tesamorelin can help to preserve the normal pulsatile pattern of GH release from the pituitary gland, acting to extend the duration of GH peaks while having less effect on peak GH levels.