Loss of Telomere Leads to p53 and Autophagy Induced Cell Death.
“autophagy-deficient cells … continued to proliferate and bypassed crisis” (2)
“In summary, cells in telomere crisis undergo cell death through autophagy, which is triggered by chromosome breakage and transduced by the cGAS–STING pathway. As cell death in crisis represents the final barrier against neoplastic transformation, a cancer therapy that involves inhibition of autophagy could be counterproductive… Moreover, cells lacking either cGAS or STING proliferated beyond crisis. “
“Autophagy mediates the turnover of cytoplasmic macromolecules to support cellular homeostasis. Autophagy generally blocks apoptosis, but in specific circumstances it can lead to cell death through excessive degradation of cell constituents. The authors studied telomere crisis using human fibroblasts and epithelial cells, in which the RB and/or p53 pathways were suppressed; these cells bypassed senescence and entered replicative stress, exhibiting telomere attrition, chromosome fusions and cell death.”
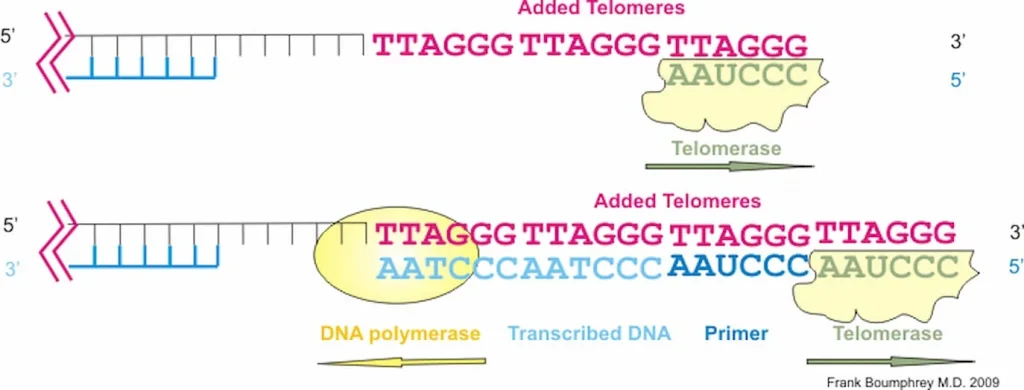
“Telomere deprotection through TRF2 depletion was sufficient to activate autophagy independently of replicative crisis, and genetic suppression of telomere fusions in TRF2-depleted cells reduced the accumulation of cytosolic DNA and attenuated autophagy, suggesting that fusion-dependent cytosolic DNA is required for the telomeric autophagy response. ” (2)
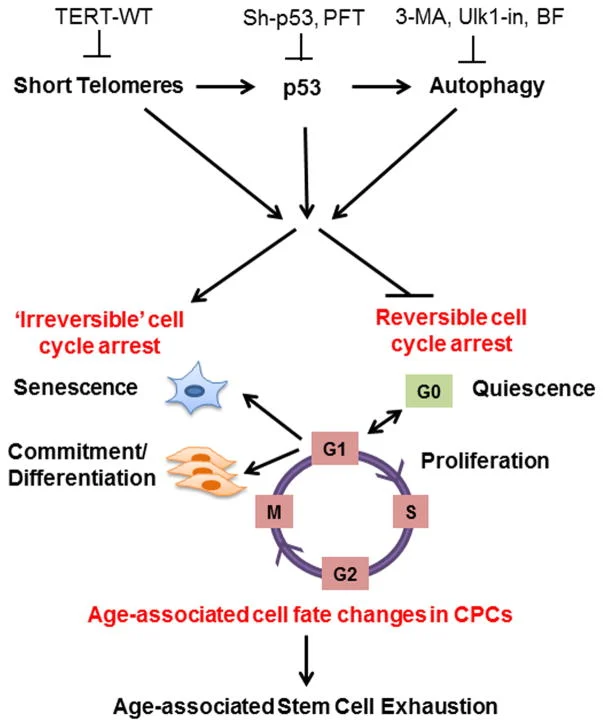
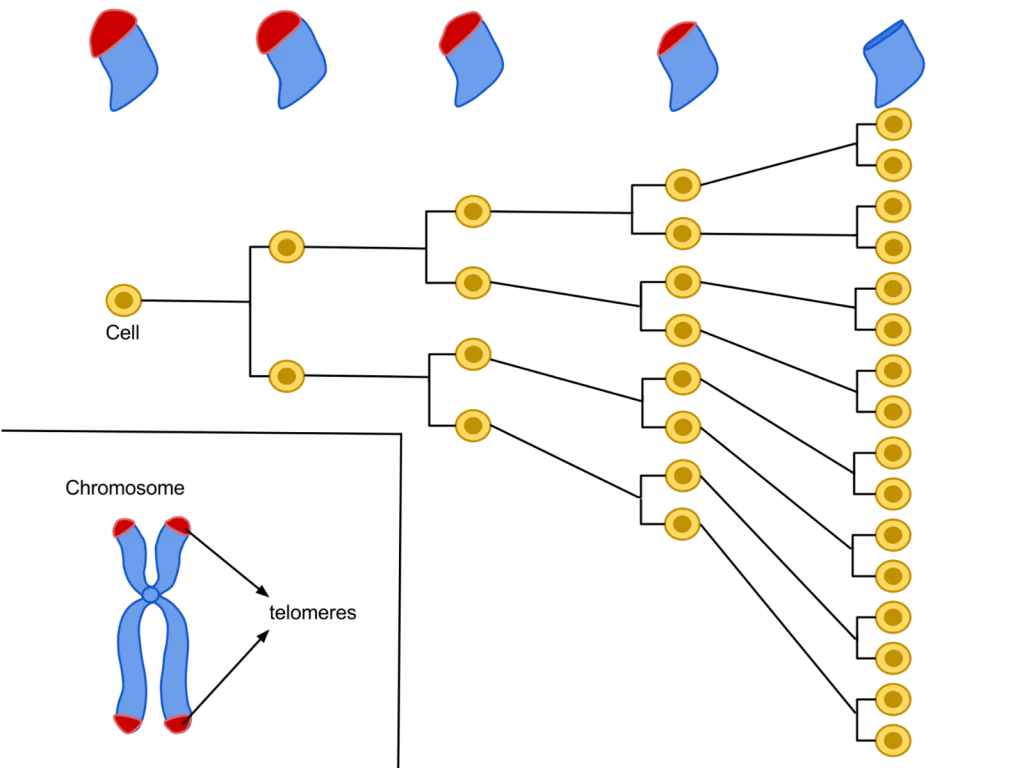
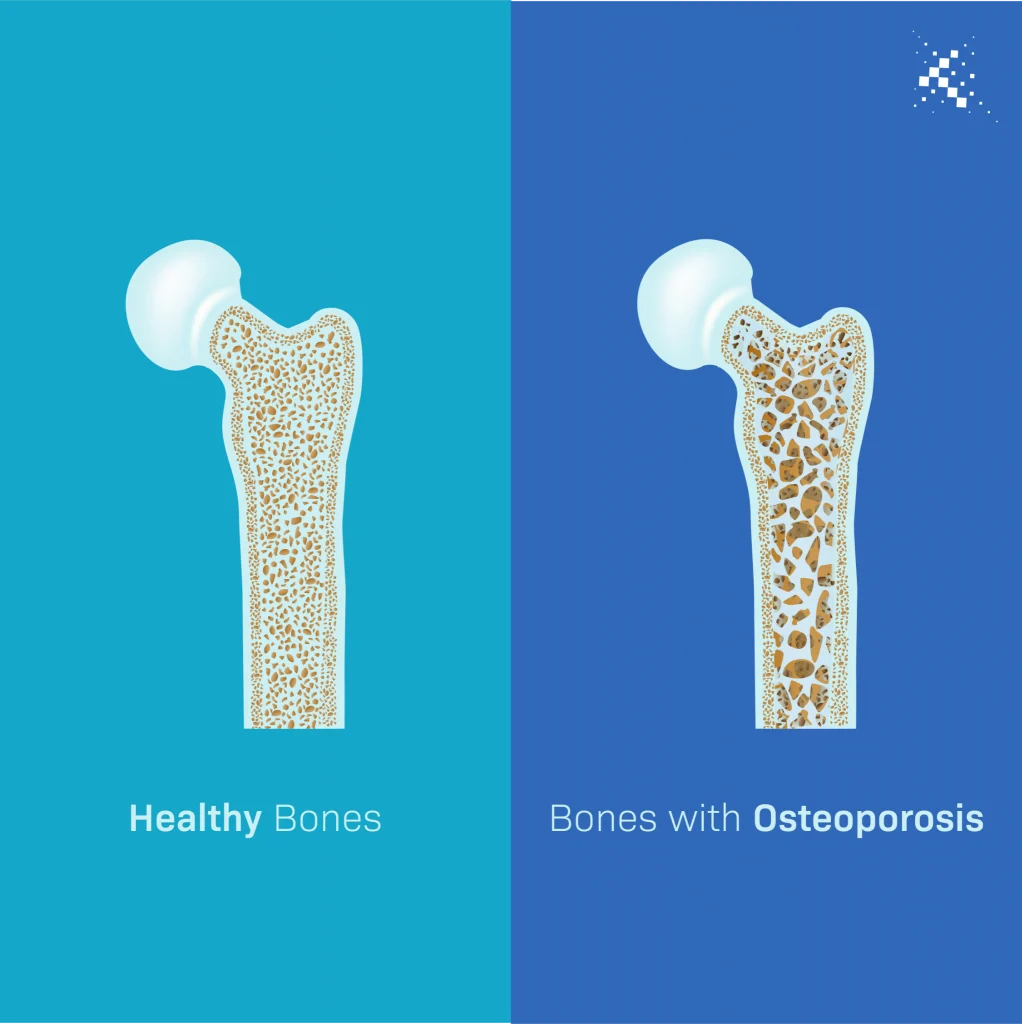
“The cell fate of CPCs changes with age and is characterized by a switch away from proliferation and quiescence (reversible form of cell cycle arrest) towards senescence and increased basal commitment (‘irreversible’ forms of cell cycle arrest) accounting for age-associated stem cell exhaustion. Mechanistically, short telomeres activate p53 that induces autophagy and at least partially contributes to the age-associated change in cell fate. Blunting telomere shortening via overexpression of TERT-WT, silencing p53 , or treating with pharmacological inhibitors of p53 (PFT) and autophagy (3-MA, Ulk1-In, BF) selectively attenuate senescence and basal commitment and reverse cell fate of aged CPCs.” (3)
Circadian Rhythm Controls Telomeres and Telomerase Activity.
“Circadian clocks are fundamental machinery in organisms ranging from archaea to humans. Disruption of the circadian system is associated with premature aging in mice, but the molecular basis underlying this phenomenon is still unclear. In this study, we found that telomerase activity exhibits endogenous circadian rhythmicity in humans and mice. Human and mouse TERT mRNA expression oscillates with circadian rhythms and are under the control of CLOCK–BMAL1 heterodimers.
CLOCK deficiency in mice causes loss of rhythmic telomerase activities, TERT mRNA oscillation, and shortened telomere length. Physicians with regular work schedules have circadian oscillation of telomerase activity while emergency physicians working in shifts lose the circadian rhythms of telomerase activity. These findings identify the circadian rhythm as a mechanism underlying telomere and telomerase activity control that serve as interconnections between circadian systems and aging.” (4)
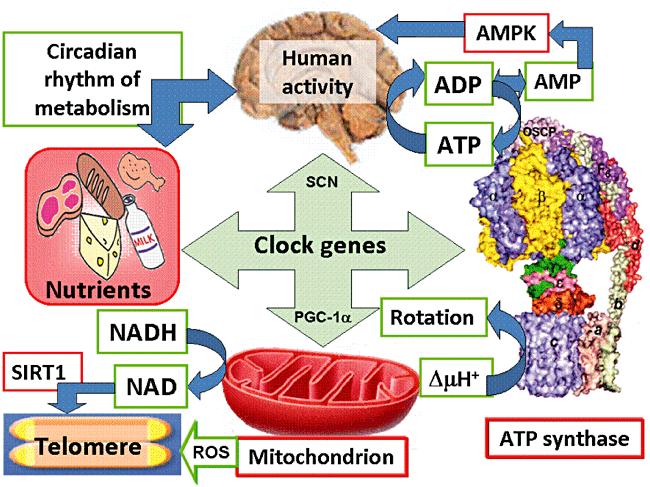
“Human activity is driven by NADH and ATP produced from nutrients, and the resulting NAD and AMP play a predominant role in energy regulation. Caloric restriction increases both AMP and NAD and is known to extend the healthspan (healthy lifespan) of animals. Silent information regulator T1 (SIRT1), the NAD-dependent deacetylase, attenuates telomere shortening, while peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α), a master modulator of gene expression, is phosphorylated by AMP kinase and deacetylated by SIRT1. Thus, PGC-1α is a key component of the circadian oscillator that integrates the mammalian clock and energy metabolism.
Reactive oxygen species produced in clock mutants result in telomere shortening. The circadian rhythms produced by clock genes and lifestyle factors are ultimately controlled by the human brain and drive homeostatic and hedonic feeding and daily activity. ” (9)
- Telomerase and TERT mRNA expressions exhibit endogenous circadian rhythm.
- Human and mouse TERT mRNA expression are under the control of CLOCK–BMAL1 heterodimers.
- CLOCK deficient mice have shortened telomere length and abnormal oscillations of telomerase activity and TERT mRNA.
- Emergency physicians working in shifts lose the circadian rhythms of telomerase activity.